[最も人気のある!] yield point definition engineering 605450-What does yield point mean
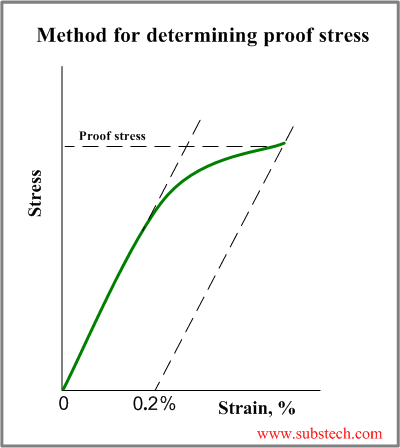
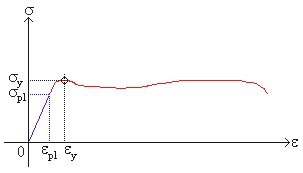
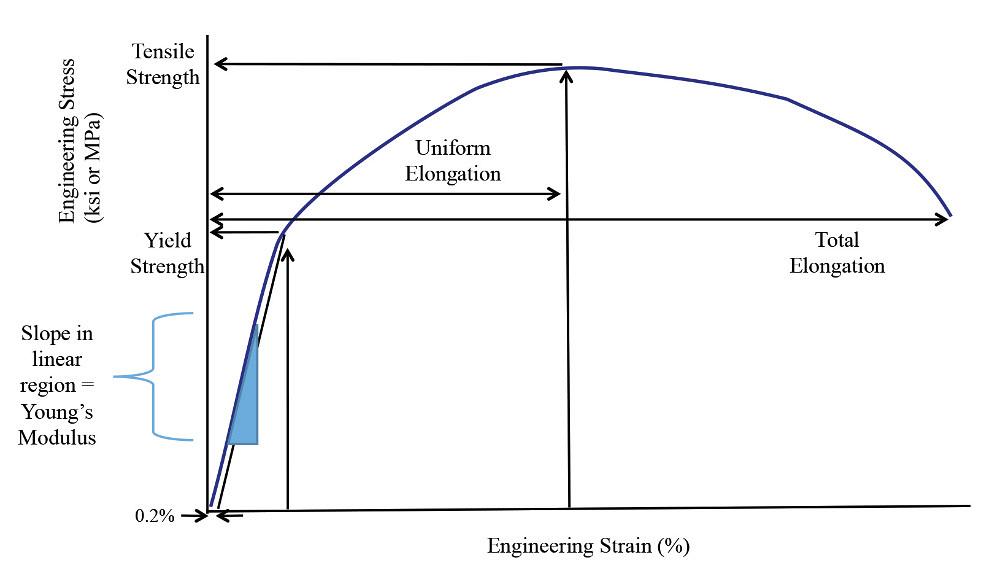
To determine the yield strength using this offset, the point is found on the strain axis (xaxis) of 0002, and then a line parallel to the stressstrain line is drawn This line will intersect the stressstrain line slightly after it begins to curve, and that intersection is defined as the yield strength with a 02% offsetYield Point The first stress in a material, less than the maximum attainable stress, at which an increase in stress Not a general term or property;Or the amount of stress in a solid at the onset of permanent deformation The yield point, alternatively called the elastic limit, marks the end of elastic behaviour and the beginning of plastic behaviour

What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
What does yield point mean
What does yield point mean-Here are a few important definitions to keep top of mind Yield strength is used in materials that exhibit an elastic behavior It's the maximum tensile stress the material can handle before permanent deformation occurs Ultimate strength refers to the maximum stress before failure occursThe difference between the cumulative volume percent at upper and lower cut points is reported as the yield (in volume %) for the particular distillate fraction For example, for the crude represented in Figure 411, the kerosene yield can be calculated as 40% (at Tb) % (Ta) = % by volume Table 41 shows the TBP cut points for crude oil distillate fractions


What Is Yield In Materials Yield Stress Yield Strength And Yield Point Materials Science Engineering
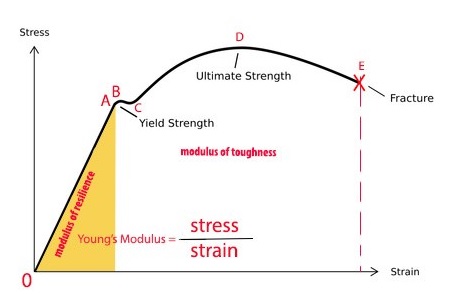
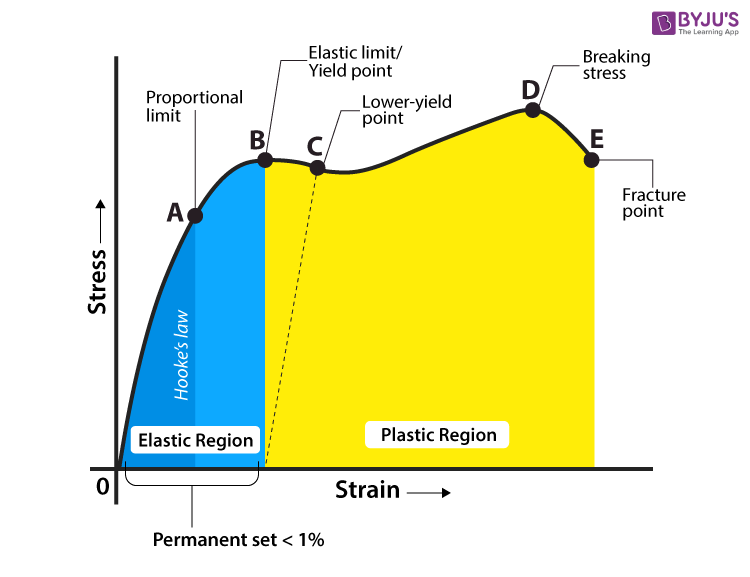
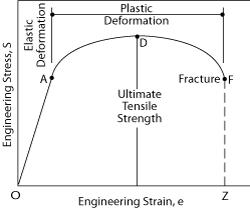
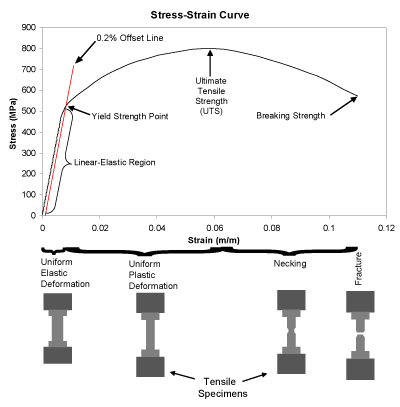
The Yield Point is in mild or mediumcarbon steel the stress at which a marked increase in deformation occurs without increase inEngineering stress and strain data is commonly used because it is easier to generate the data and the tensile properties are adequate for engineering calculations When considering the stressstrain curves in the next section, however, it should be understood that metals and other materials continues to strainharden until they fracture and the(iii) Yield Point The yield point is defined as the point at which the material starts to deform plastically After the yield point is passed, permanent plastic deformation occurs There are two yield points (i) upper yield point (ii) lower yield point (iv) Ultimate Stress Point It is a point that represents the maximum stress that a
The parameters, which are used to describe the stressstrain curve of a metal, are the tensile strength, yield strength or yield point, percent elongation, and reduction of area The first two are strength parameters;Therefore, the yield point is an approximate estimate of the elastic limit of the material In this case, we simply project a horizontal line from the yield point to the yaxis of the stressstrain curve to get the value of the yield stress However, in some other steels determining the yield stress graphically is not as straightforwardThe last two indicate ductility The general shape of the engineering stressstrain curve (Fig 1) requires further explanation
Engineering, the application of science to the optimum conversion of natural resources to the uses of humankind Engineers employ two types of natural resources—materials and energy Engineers must concern themselves with the continual development of new resources as well as the efficient use of existing onesThe definition of YPE then became "the difference between the elongation at the yield point and the last inflection point" Given the formalized definition of discontinuous yielding, it became necessary to develop an algorithm for the calculation of first and second derivativesMethod was used to determine the material yield strength from the engineering stressstrain curve Because the tensile testing was focused on development of continuous engineering stressstrain curves to failure, at the sacrifice of an accurate yield point definition, many of the resulting curves did not display a distinct modulus


What Is Yield In Materials Yield Stress Yield Strength And Yield Point Materials Science Engineering


Stress Versus Strain
Only certain metals exhibit a yield pointYield strength is defined in engineering as the amount of stress (Yield point) that a material can undergo before moving from elastic deformation into plastic deformation Yielding a material deforms permanently;YP ⇒ Yield Point Stress at which there are large increases in strain with little or no increase in stress Among common structural materials, only steel exhibits this type of response σ YS ⇒ Yield Strength The maximum stress that can be applied without exceeding a specified value of permanent strain (typically 2% = 002 in/in)
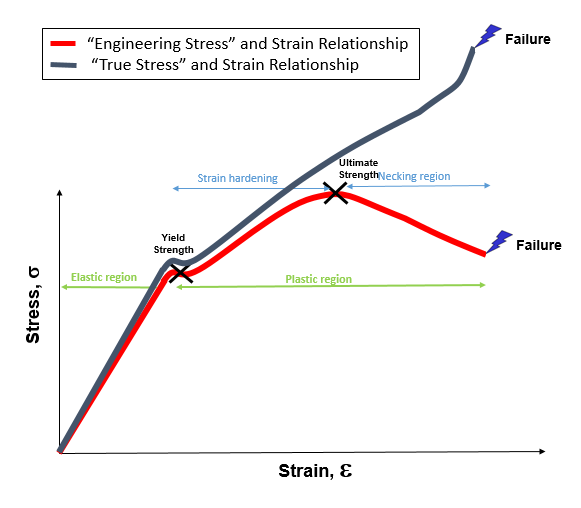


Engineering Stress And Strain Curve Diagram


Solved 1 Define A Homogeneous Material 2 The Modulus Of Chegg Com
Yield Strength is the stress a material can withstand without permanent deformation or a point at which it will no longer return to its original dimensions (by 02% in length) Whereas, Tensile Strength is the maximum stress (usually represented in PSI) that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before failing or breakingYield (verb) To produce as a result "Adding 3 and 4 yields a result of 7" Yield (verb) To produce a particular sound as the result of a sound law "IndoEuropean p yields Germanic f" Yield (verb) To pass the material's yield point and undergo plastic deformation Yield (verb) To admit to be true;This region starts as the strain goes beyond yield point, and ends at the ultimate strength point, which is the maximal stress shown in the stressstrain curve In this region, the stress mainly increases as material elongates, except that there is a nearly flat region at the beginning



Ultimate Tensile Strength Importance Testing Examples Fractory


Q Tbn And9gctk9iq8odyr8oad6ztec3f7a2cfwevlxhbui8zaefsdyzdh0s1n Usqp Cau
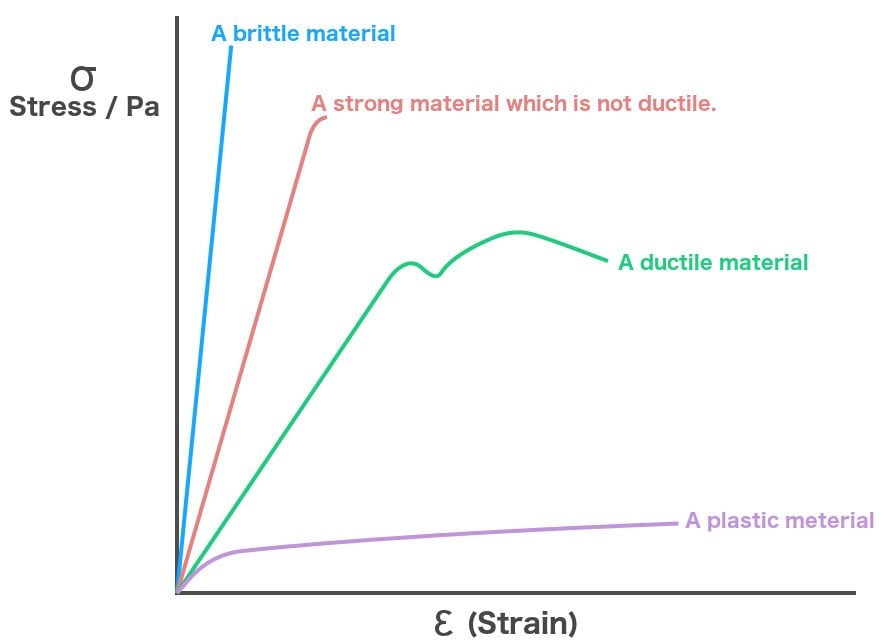
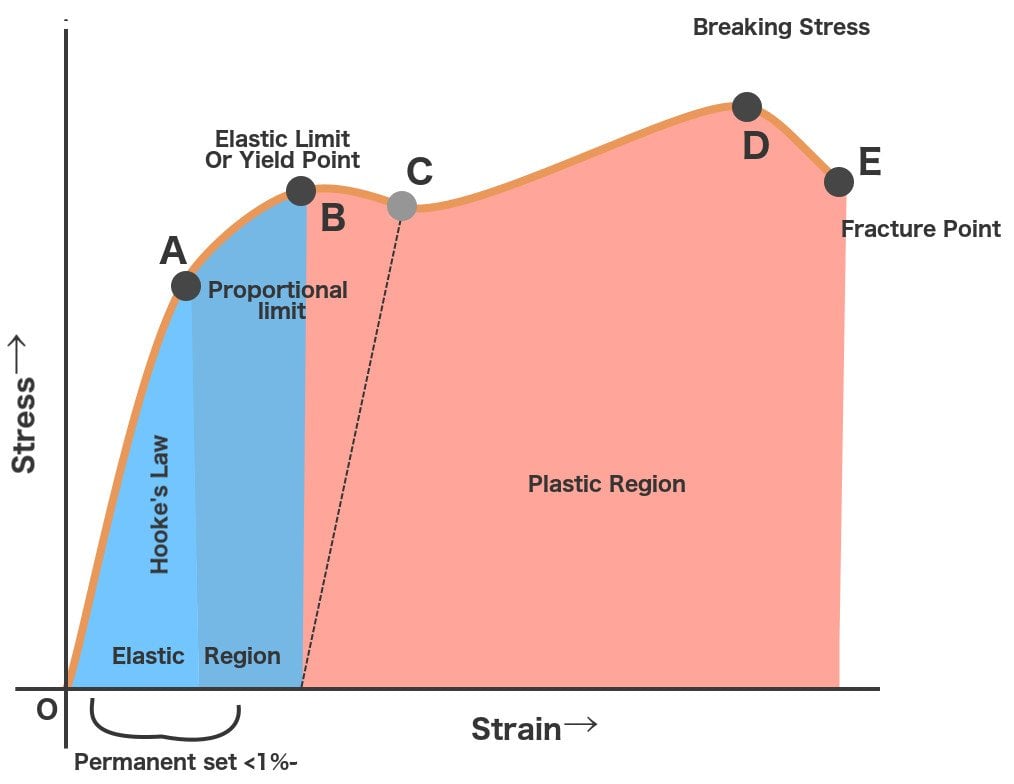
In this ductile material curve, you can see a point labeled yield strength, also known as yield point The dip in the curve at this point is an indication that the material has yielded or deformedThe point C is termed as Yield Point Between B and C, material becomes plastic ie, if applied force is removed from any point between B and C, material will not regain its original shape and size The extension not recoverable after the removal of applied force is called as permanent setYield strength is used in materials that exhibit an elastic behavior It's the maximum tensile stress the material can handle before permanent deformation occurs Key point Both materials are equally strong, but the metal is stiffer than the polymer Welcome to Engineering Heroes a series where we interview the mechanical engineers
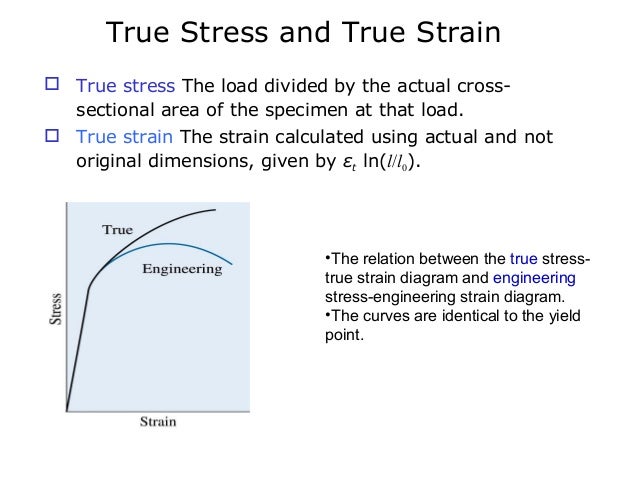


Mechanical Properties
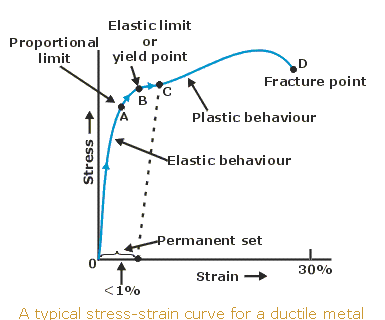


Steps To Analyzing A Material S Properties From Its Stress Strain Curve 9 Steps Instructables
Engineering Dictionary Search engineering dictionary Definition Yield Point 2 The first stress in a material, usually less than the maximum attainable stress, at which an increase in strain occurs without an increase in stress Only certain metals exhibit a yield point If there is a decrease in stress after yielding, a distinction may beYield strength can be explained, in engineering and materials science, as the stress at which a material begins to plastically deform Prior to the yield point, the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removedYield Point and Offset Yield Point The point on the engineering stress strain from ME 2140 at Tarrant County College
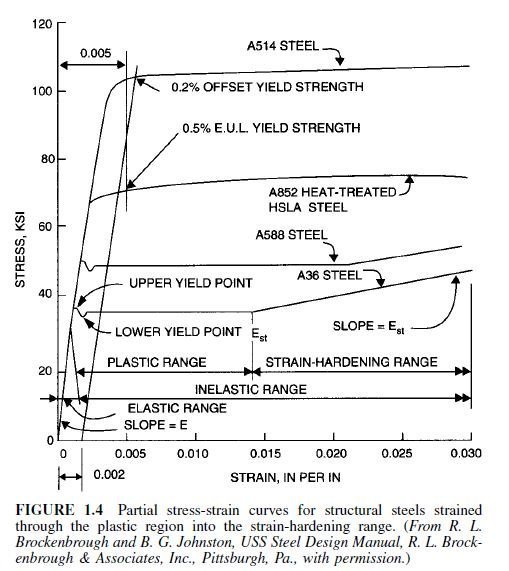


Yield Point Civil Engineering
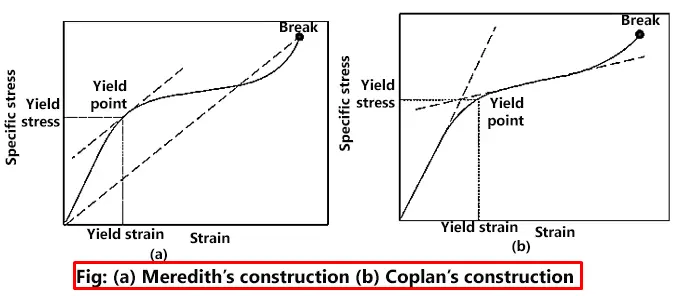


Tensile Testing Terms And Tensile Testing Terms Definitions Textile Study Center
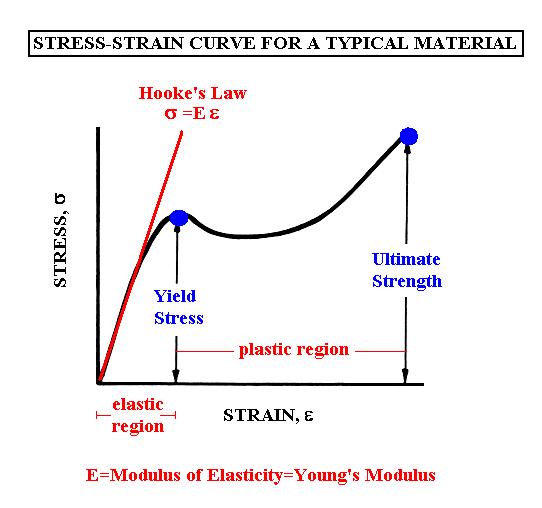
The Yield Point is in mild or mediumcarbon steel the stress at which a marked increase in deformation occurs without increase in load In other steels and in nonferrous metals this phenomenon is not observedAdditionally, you can convert an engineering stressstrain curve into a true stressstrain curve in the region between the yield point and UTS with the equations References and Further Reading 1 Kalpakjian, Serope and Steven R Schmid (14), Manufacturing Engineering and Technology (6th ed),A yield strength or yield point is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically Prior to the yield point the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed Once the yield point is passed, some fraction of the deformation will be permanent and nonreversible



What Is Yield In Materials Yield Stress Yield Strength And Yield Point Materials Science Engineering



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge
The volume occupied by one sack of dry cement after mixing with water and additives to form a slurry of a desired density Yield is commonly expressed in US units as cubic feet per sack (ft3/sk) 2Engineering Dictionary Search engineering dictionary Definition Yield Point 3 The load per unit of original cross section at which, in soft steel, a marked increase in deformation occurs without increase in loadYield Point 2 The first stress in a material, usually less than the maximum attainable stress, at which an increase in strain occurs without an increase in stress Only certain metals exhibit a yield point If there is a decrease in stress after yielding, a distinction may be made between upper and lower yield points


Difference Between Yield Strength And Tensile Strength


What Is The Difference Between The Yield Strength Re And The Practical Limit Rp Of A Material Quora
YP is the yield stress extrapolated to a shear rate of zero (Plastic viscosity, PV, is the other parameter of the Binghamplastic model) A Bingham plastic fluid plots as a straight line on a shear rate (xaxis) versus shear stress (yaxis) plot, in which YP is the zeroshearrate intercept (PV is the slope of the line)Lesson 10 Yield Point Definition, Curve & Elongation Take Quiz Lesson 11 What is an Alloy?Yield Point = Y P = 300 RPM Reading Plastic Viscosity (B) GEL STRENGTH Theory The Baroid Rheometer is also used to determine the Gel strength, in lb/100 sq ft, of a mud The Gel strength is a function of the interparticle forces


Property Information


Yield Strength Defintion Examples And A Simplified Explanation
08/10/12 13 MSc Textile Engineering – AY 1213 Ada Ferri 14 Yield point • Depending on the material being tested, the curve often contains a point where a marked decrease in slope occurs This point is known as the yield point At this point important changes in the force elongation relationship occurThe yield point elongation is therefore an inhomogeneous plastic deformation Figure Lüder bands (stretcher strain marks) Once the tensile test specimen has been stretched beyond the range of the Lüder strain, the yield point effect no longer occurs if the tensile test is repeated in a timely mannerThe definition of YPE then became "the difference between the elongation at the yield point and the last inflection point" Given the formalized definition of discontinuous yielding, it became necessary to develop an algorithm for the calculation of first and second derivatives



Ultimate Tensile Strength Wikipedia



Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Strain Curve
Additionally, you can convert an engineering stressstrain curve into a true stressstrain curve in the region between the yield point and UTS with the equations References and Further Reading 1 Kalpakjian, Serope and Steven R Schmid (14), Manufacturing Engineering and Technology (6th ed),In Wikipedia, yield point is stated as follows A yield strength or yield point is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically Prior to the yield point the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removedYield Point and Offset Yield Point The point on the engineering stress strain from ME 2140 at Tarrant County College



What Is Yield Strength Of Any Material Hindi Urdu Yield Strength क य ह Youtube
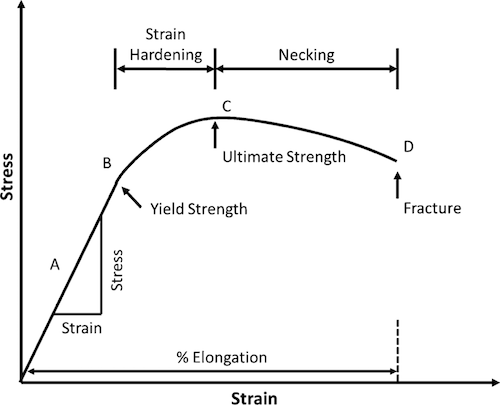


Cee 3710 Strength Versus Stiffness
In materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed Once the yield point is passed, some fraction of the deformation will be permanent andA straight line is drawn through Point (D) at the same slope as the initial portion of the stressstrain curve The point of intersection of the new line and the stressstrain curve is projected to the stress axis The stress value, in pounds per square inch, is the yield strength It is indicated in Figure 5 as Point 3Let's understand the meaning of "Yield" first Yield point tells us a very interesting story about the failure of a structure or material In our highschool, we have read about Hooke's law It says that stress is proportional to strain up to a ce



What Is The Difference Between Elastic Limit And Yield Point Physics Stack Exchange



Stress Strain Curves Of Metallic Materials And Post Necking Strain Hardening Characterization A Review Tu Fatigue Amp Fracture Of Engineering Materials Amp Structures Wiley Online Library
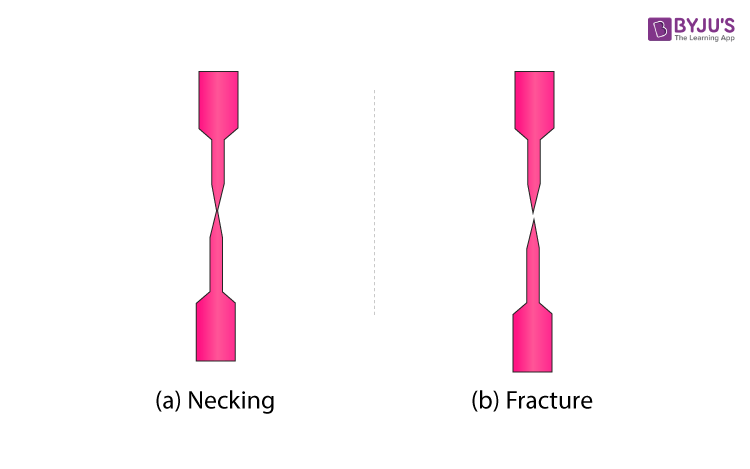
There is a point when an increase of strain is not provoked by an increase of stress on the test specimen ie beyond which the plastic material stretches briefly without a noticeable increase in load This point is known as the yield point Most unreinforced materials have a distinct yield point Reinforced plastic materials exhibit a yield regionThe point of failure, or permanent deformation, of a component, due to a specific amount of force The failure occurs at the yield point of the material, measured in force ( pounds of pressure ) All materials have different yield points, and these yield points are an important characteristic which determines how a material is used as a construction componentYS or yield point is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically Prior to the yield point the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed


What Is Yield In Materials Yield Stress Yield Strength And Yield Point Materials Science Engineering



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
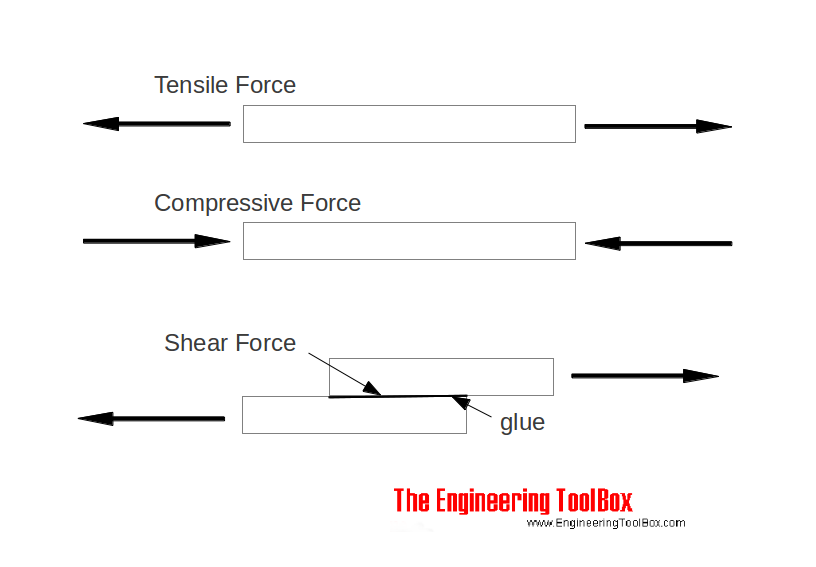
To allow Yield (noun) PaymentAs the stress point is inside the yield surface, ie, f < 0, the material is elastic The plasticity initiates when the stress point reaches the yield surface, ie, f = 0, and it continues as far as the point remains on the yield surface, which is defined as loading However, if the stress point goes back inside the yield surface, plastic deformation stops, and the deformation becomesYield point, in mechanical engineering, load at which a solid material that is being stretched begins to flow, or change shape permanently, divided by its original crosssectional area;


Exploring The Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel The Chicago Curve


Effects Of Finish Rolling Temperature And Yield Ratio On Variations In Yield Strength After Pipe Forming Of Api X65 Line Pipe Steels Scientific Reports
It forms part of the overall topic of Yield and Yield Criteria I see the whole structure of various related articles as Plasticity (physics) being the starting point Yield (engineering) as a subarticle In the later the topics of yield criterion, yield curve, yield surface, flow rule, associated and nonassociated flow rule, etc, would bePoint (BC) is the yield point on the graph and stress associated with this point is known as yield stress Ultimate Stress Point (D) Ultimate stress point is the maximum strength that material has to bear stress before breaking It can also be defined as the ultimate stress corresponding to the peak point on the stressstrain graphIn this ductile material curve, you can see a point labeled yield strength, also known as yield point The dip in the curve at this point is an indication that the material has yielded or deformed


Tensile Test And Stress Strain Diagram Substech


Finding 0 2 Offset Strain Dplot
Definition & Examples Lesson 1 Engineering Stress Definition & EquationYield strength is defined in engineering as the amount of stress (Yield point) that a material can undergo before moving from elastic deformation into plastic deformation Yielding a material deforms permanently;



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com


2



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv



What Is The Difference Between Upper Yield Point And Lower Yield Point Of A Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Quora



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com


Engarc L Offset Yield Method



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs
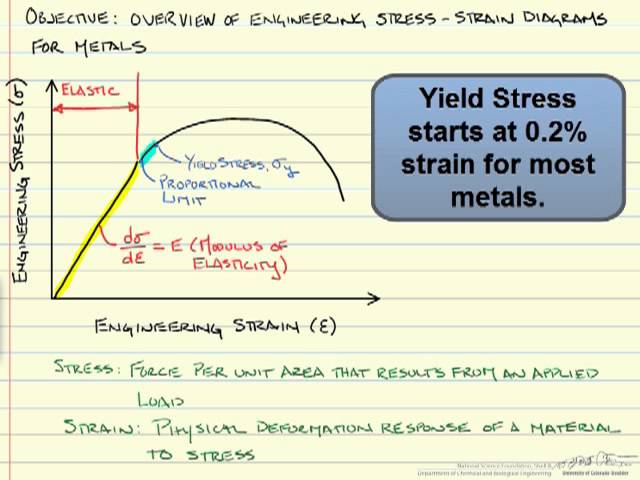


Stress Strain Diagrams Youtube



Stress Strain Curve Definition Examples Diagrams



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv



What Is Proof Stress Civildigital


Engineering Stress Strain Curve



Strength At Break Tensile


Q Tbn And9gcrdlwvzddnehsqd3q4pa68yhsrtz2zujhc4jj P3hg9jteevyia Usqp Cau



Strain Ageing Of Steel Part One Total Materia Article



Hooke S Law And Stress Strain Curve Analysis Videos And Examples
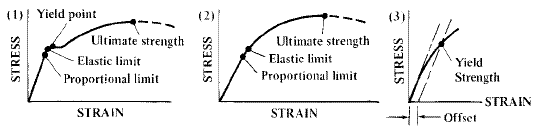


Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Permanent Set Point Vs Elastic Limit Physics Stack Exchange
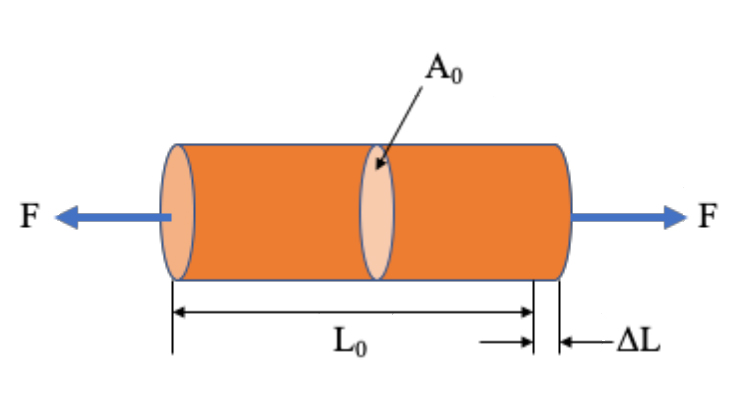


Stress And Strain Mechanical Properties Of Materials



Mechanical Testing Tensile Testing Part 1 Twi
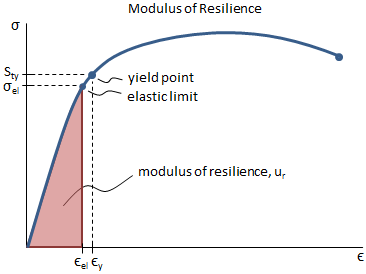


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



Materials Science



What Is The Difference Betweem True Stress And Flow Stress



Materials Testing Glossary Admet


Www Usna Edu Naoe Files Documents Courses En380 Course Notes Ch10 Deformation Pdf



Yield Engineering Wikipedia


What Is Yield In Materials Yield Stress Yield Strength And Yield Point Materials Science Engineering



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Stress And Strain Mechanical Properties Of Materials



Materials Testing Glossary Admet



Yield Point An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Stress Strain Curve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


What Is The Difference Between Ultimate Stress And Yield Stress Quora



What Is Tensile Testing Instron


Yield Strength Defintion Examples And A Simplified Explanation



Minimum Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Strength



Yield Strength Of Plastics Basic Principles The Tensile Test And Material Property Table Engineeringclicks


Stress Strain And Young S Modulus



Inhomogeneous Deformation


Strength And Stiffness Characteristics
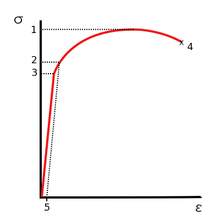


Ultimate Tensile Strength Wikipedia
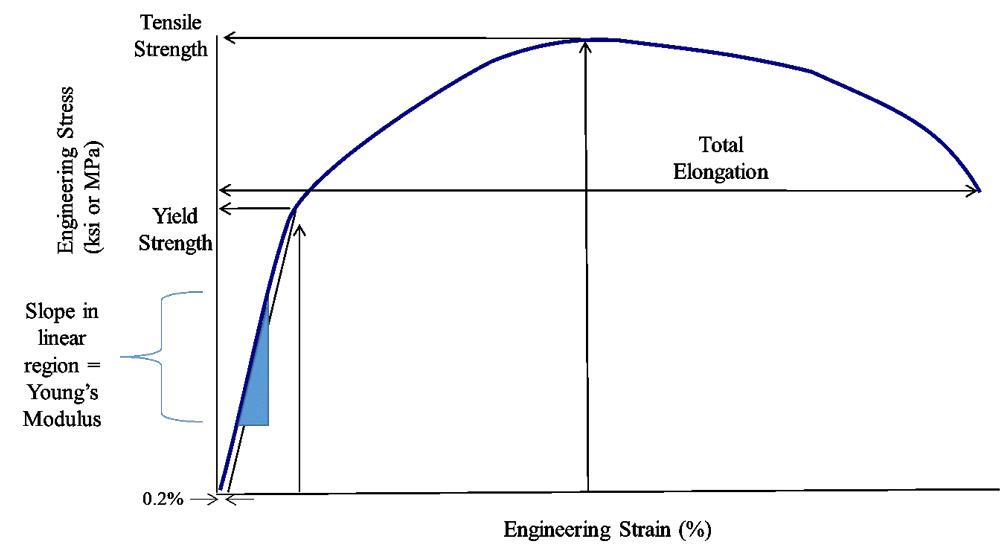


The Differences Between Stiffness And Strength In Metal



Yield Point Instron


Figure 6 Definition Of Yield Point Correlation Between Engineering Stress Strain And True Stress Strain Curve Science And Education Publishing
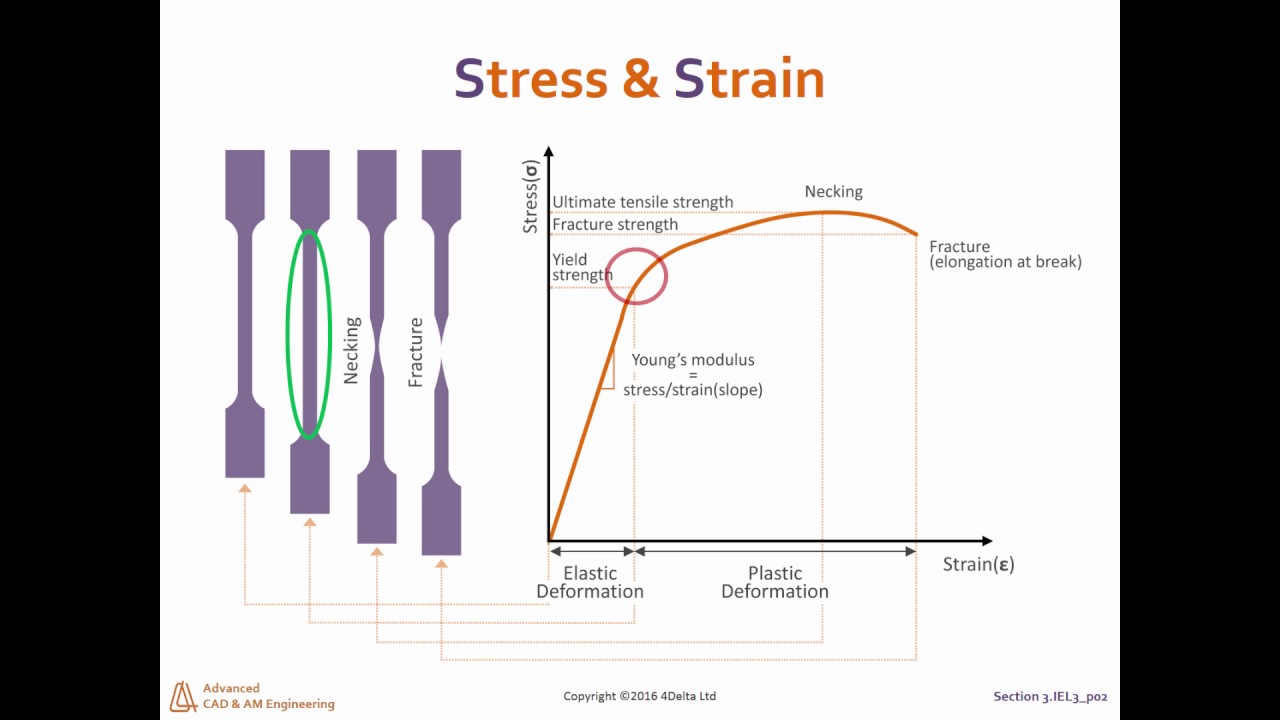


Yield Stress Yield Strenght Youtube
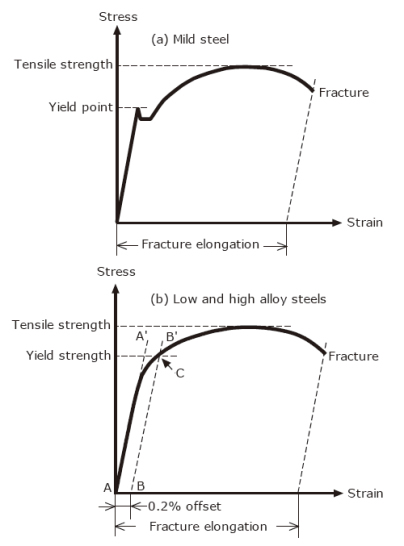


The Abc S Of Arc Welding Education Center Kobelco Kobe Steel Ltd


Q Tbn And9gcrdlwvzddnehsqd3q4pa68yhsrtz2zujhc4jj P3hg9jteevyia Usqp Cau



Engineering Stress Strain Curve Vs A True Stress True Strain Curve Download Scientific Diagram



Yield Strength R Sub El Sub N Mm Sup 2 Sup Bossard Group



Why Does The Stress Strain Curve Decrease Engineering Stack Exchange


The Strain Rate Effect Of Engineering Materials And Its Unified Model



What Is The Yield Point In A Stress Strain Diagram Quora


Material Properties Basic Science Orthobullets


Getting To Know More About The Metal You Are Forming


Nondestructive Evaluation Physics Materials


Q Tbn And9gct7joip1zorpu6bihpumnu2inmskqjwy3j5qlq Et5h4v2gkntg Usqp Cau



Determining Tensile Test Offset Yield Strengths Using Extensometer Admet



Predicting Structural Instability Due To Plastic Hinge Collapse Mechanism Digital Engineering 24 7



Yield Engineering Pdf Yield Engineering Dislocation



What Is The Difference Between Upper Yield Point And Lower Yield Point Of A Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Quora



How To Measure Tensile Strength Elastic Modulus And Ductility Rolled Alloys Inc


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia



Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Strain Curve


Stress Versus Strain
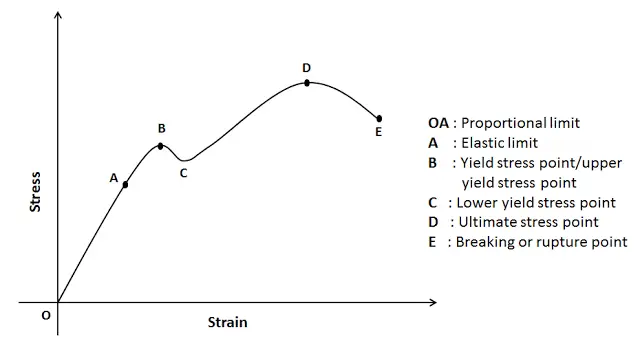


Stress Strain Curve Relationship Diagram And Explanation Mechanical Booster



Yield Point Definition Curve Elongation General Class Study Com
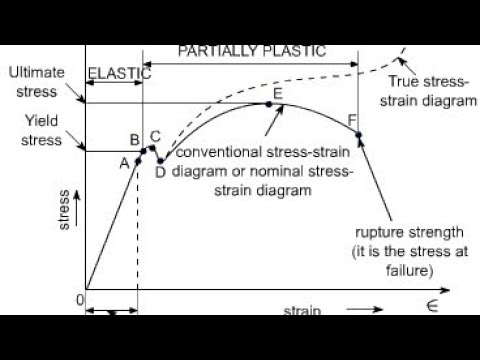


Stress Vs Strain Curve Yield Point Yield Strength Elastic Limit Neking Ultimate Tensile Youtube



What Is The Difference Between Upper Yield Point And Lower Yield Point Of A Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Quora



Resilience Resilient Material



3 1 4 A Bit More About Tensile Testing



Definition Of Mos
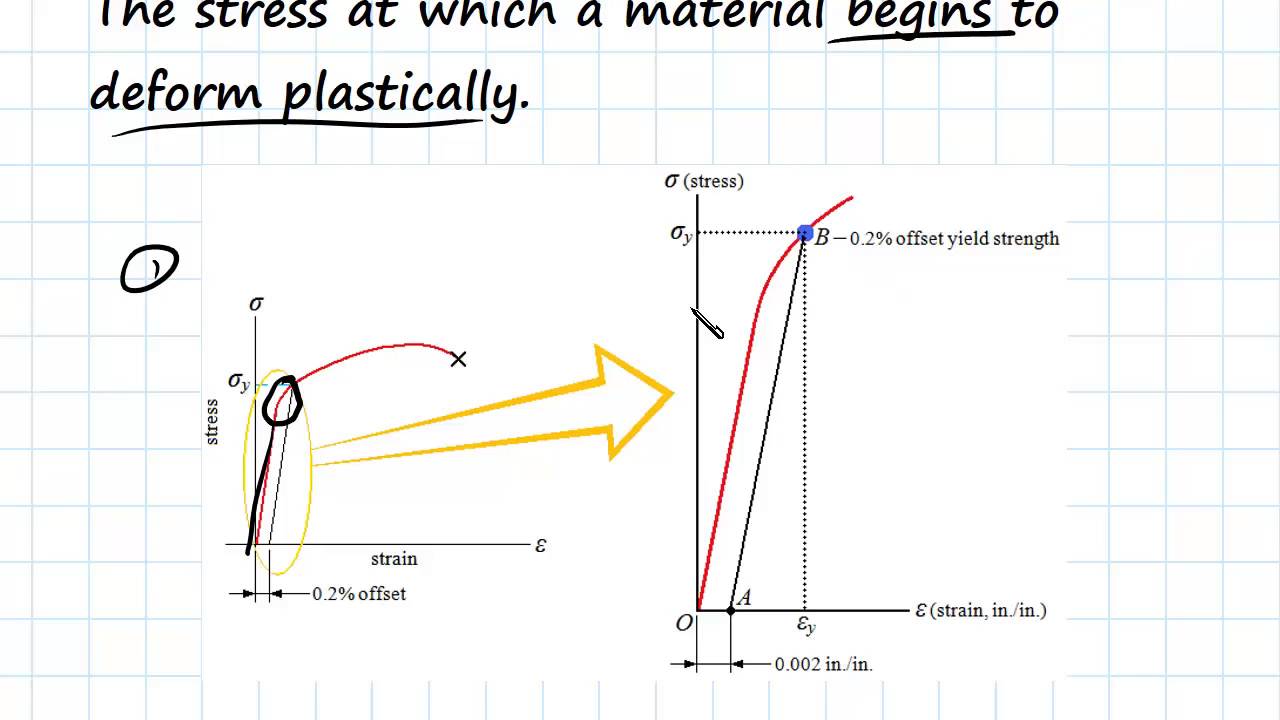


Yield And Tensile Strength Engineering Materials Youtube



Yield Stress Of A Material Simple Explanation Civildigital


コメント
コメントを投稿